Managing a project professionally means managing to increase the chances of meeting the project management goals, at the end of the project. Professional Project Managers try to ensure projects finish on time, on budget, delivering the artefacts inside the scope and no others, with the expected quality, etc.
In practice, this is all done by the project team members collaborating on tasks. But good collaboration does not imply necessarily project success. Many good teams perform badly on projects. Not the fault of the project team, the project ends up as a failure: over cost, delays, bad quality, unfulfilled expectations, unhappiness… If a project is due, for instance, in 6 months but it takes finally 12, with no added budget, this could mean the project margin may go down from, let’s say, an expected +20% to an achieved -50%. This totally kills the financial result of the project, but it could also damage the financial goals of a program, a portfolio, a business unit, etc. If this happens on several projects, or many of them, then the organization is possibly on the need of firing people, or even worse, having to close.
Effective collaboration among people is always needed, but when people are project team members, then you need a professional project manager accountable. A research by PMI predicts that the number of individuals working in project-based roles will increase from 66 million in 2017 to 88 million in 2027.
Professional project managers use their soft skills to lead the predictive or agile project, to engage stakeholders, to fulfill expectations from managers and customers, etc. They also user their hard skills to manage scope, schedule, funding, cost, risk, procurement, etc.
Which soft skills would be the right to use? It depends on the group of stakeholders, always different at each project. No generic rule applicable here.
However, there are generic rules applicable regarding the hard skills for project managers, many of them highly automatable, making professional project management easier. This is good news!
From our point of view, three techniques are quite important to control the project performance:
1) Decomposition
The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) shows how the project is broken down into manageable units named “work packages”.
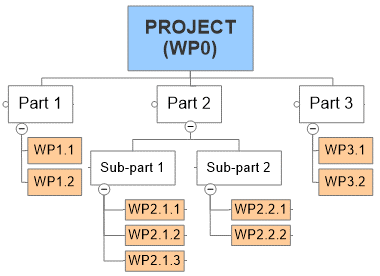
Project work packages facilitate proper schedule planning, cost estimation, resource assignation, etc. When problems arise, it is effective to focus analysis and solutions on the level of the work packages impacted, to propose preventive or corrective actions properly.
In PMPeople, work packages can contain tasks, deliverables, requirements, stories, milestones, etc. Let’s see some features related to work packages:
- If a project is not decomposed into parts, it can be referred as a work package itself. We use the name work package 0 for the project as a whole.
- Optionally, project can be decomposed into as many work packages as needed to facilitate management. Following the 100% rule, the sum of the work at the work package level equals the 100% of the project work. In other words, if the project is correctly decomposed, work packages cover the totality of work, exactly.
- PMPeople can import work packages from any scheduling management tool Microsoft Project compatible, such as Primavera, Smartsheet, ProjectLibre, etc. These tools can export task data (name, description, dates, costs, priorities, etc.) to an XML file. If task priority is set to “1”, then these data will be uploaded inside a work package in PMPeople.
- Project baselines of scope, schedule, funding and cost, can be controlled at the level of each work package.
- Project team members can submit hours and expenses at the level of the work package.
- Many other data is also related to a work package: calendars, change requests, issues, risks, comments, feedback, etc.
2) Controlling the Project Schedule Performance
Project managers report status reports periodically. Steering committees are always interested on schedule performance. Project managers measure the cumulated variances so far and they can also forecast variances at the end, in order to take corrective or preventive actions to save time. They use three couples of dates for each work package and for the project itself:
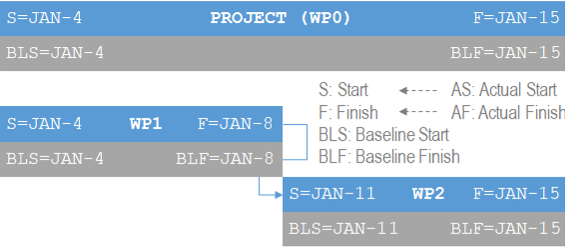
- Baseline Start and Baseline Finish: start and finish committed dates.
- Actual Start and Actual Finish: to register the actual start and finish when things really happen.
- Start and Finish: to annotate the best estimate of dates for starting and finishing work. These values should be updated whenever better forecast is known.
This video shows how to use PMPeople to control project schedule performance:
3) Controlling the Project Cost Performance
Earned Value Management (EVM), is an ANSI 748 standard to control the project cost performance. According to EVM standard, we can measure three data values to control the project cost performance, as of each status date:
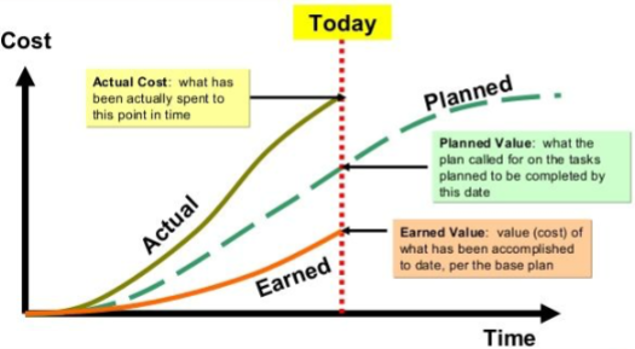
- Planned Value (PV) or Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled (BCWS) is the authorized budget assigned to scheduled work, up to status date. At project closing, PV equals Budget at Completion (BAC).
- Earned Value (EV) or Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP) is the measure of work performed expressed in terms of the budget authorized for that work, up to status date. At project closing, EV equals Budget at Completion (BAC), so as the PV.
- Actual Cost (AC) or Actual Cost of Work Performed (ACWP) is the realized cost incurred for the work performed on an activity up to status date. At project closing, AC equals the total money spent.
EVM allows measuring variances so far and forecast at the end. These data can help the project steering committee to make decisions and take corrective or preventive actions aimed to save money.
PMPeople tool makes managers use EVM standard easily, also including the metrics on earned schedule. Managers accessing the project can check cost performance online, at each review date, with charts like these below:
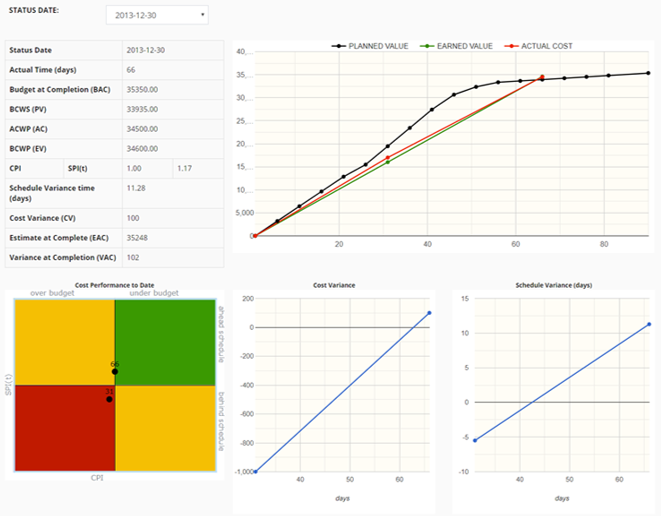
This video shows how to use PMPeople to control project cost performance:
PMPeople is the tool for the project economy. It is aimed to unify professional project management by these differential points:
- Designed by and for professional project managers, following professional project management standards.
- Online productivity –less meetings, less documents, less workflows– through distributed collaboration among 12 specialized roles: Organization Owner, 6 roles on demand management and 5 roles on supply management.
- Freemium product –unlimited time, unlimited users, only managers have to pay– usable via web and mobile application.
Start using PMPeople for free, for unlimited time and for any number of users. In premium organizations, only managers have to pay. Several roles –stakeholders, team members, sponsors and resource managers– are always free. You can increase or decrease your premium seats according to the organization actual needs. Premium organizations have access to our interactive support through Slack. Our servers are located in EU. This software can also be hosted on customer premises.
Jose Barato
Related posts
Categories
- Business (16)
- Demand Management Roles (14)
- Frequently Asked Questions (7)
- Guide (26)
- People (23)
- Assignments (2)
- Feedback (2)
- Project Team (3)
- Tracking Time And Expenses (2)
- Process (9)
- Closing (2)
- Executing And Controlling (2)
- Planning (1)
- Project Management (67)
- Management Frameworks (18)
- Organization Owner (OO) (3)
- Project Economy (54)
- Tools (19)
- Supply Management Roles (5)
- Training (6)
- Uncategorized (1)




